What Buyers Usually Gain
- Clear incoming raw material control and lot traceability
- Defined firing curves and documented kiln schedules
- Consistent testing routines (e.g., CCS, porosity, density)
- Corrective action cycles when deviations occur

In high-temperature industrial kilns, a single weak link in the refractory lining can trigger unplanned shutdowns, product quality drift, and safety risks. For buyers comparing “high alumina brick” options across global suppliers, international certifications offer a practical decision framework—especially when performance claims look similar on paper. This article explains how ISO 9001 and CE compliance connect to measurable kiln reliability, and how a 75%+ Al2O3 grade can be selected with confidence for demanding thermal and chemical conditions.
“High alumina” is a category, not a guarantee. Two bricks can both claim high Al2O3 content, yet differ significantly in bulk density, open porosity, cold crushing strength (CCS), thermal shock resistance, and consistency between batches. That consistency is where international management and conformity systems become commercial value: fewer installation surprises, fewer hot spots, and more predictable campaign life.
For global procurement teams, certifications also streamline vendor qualification. They indicate the supplier is operating with documented processes, controlled traceability, and auditable QA routines—reducing the “hidden cost” of rework, claims, and kiln downtime.
RS Refractory (Rongsheng Refractory Materials Factory) is widely recognized in the kiln refractory segment as a National High-Tech Enterprise with over 20 years of R&D and production experience. Its portfolio is commonly selected by overseas buyers seeking ISO 9001 quality management and CE conformity as part of supplier onboarding.
RS’s high-performance alumina refractory bricks are engineered to meet demanding kiln environments, with flagship grades featuring Al2O3 content above 75%—a key baseline for high-temperature stability, slag resistance, and structural strength in many industrial lining designs.
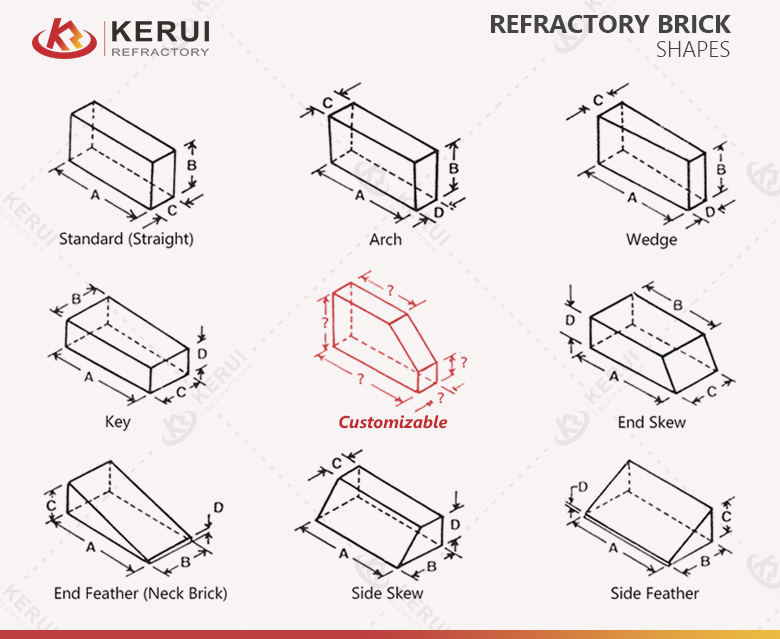
ISO 9001 is not a “performance label” for a specific brick; it is a quality management system that controls how performance is produced—batch after batch. For high alumina refractory bricks, ISO 9001 typically correlates with more stable manufacturing variables that directly influence kiln behavior.
CE marking is frequently required in EU-related procurement and projects where conformity documentation is necessary for audits and compliance workflows. For refractory buyers, CE-related processes improve clarity around product identification, declared characteristics, and supplier responsibility—particularly important when refractory bricks are used in regulated industrial facilities.
The business benefit is speed: fewer compliance back-and-forth cycles, easier approval from engineering teams, and faster integration into project documentation packs.
Certifications help validate process control, but buyers still need performance evidence tied to the kiln’s thermal and chemical reality. Below is a buyer-friendly checklist used in many RFQs for 75%+ alumina refractory brick selections.
| Key Parameter | Typical Reference for 75%+ Al2O3 | Why It Affects Kiln Stability | What to Ask the Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 Content | ≥ 75% | Supports refractoriness and slag resistance at high heat load | Test report by batch; chemical analysis method and tolerances |
| Refractoriness | ~ 1750–1790 °C | Reduces softening risk in hot-face zones | Standard used; results across multiple production lots |
| Cold Crushing Strength (CCS) | ~ 70–100 MPa | Improves structural integrity under mechanical and thermal stress | CCS average + minimum; acceptance criteria in QC |
| Apparent Porosity | ~ 16–22% | Lower porosity often means better corrosion resistance and lower penetration | Porosity + bulk density; how they control firing consistency |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Common target: 20–30 water-quench cycles (reference) | Helps resist spalling during frequent start-stop or load changes | Test method and historical performance in similar kilns |
Note: Reference figures vary by formulation and standard; buyers should match targets to kiln zone (hot face, transition, backup lining) and operating profile.
Industrial kiln linings fail more often from combined stresses than from temperature alone: molten slag infiltration, alkali vapor attack, rapid temperature swings, and mechanical abrasion can work together. High alumina bricks with 75%+ Al2O3 are commonly chosen because they offer a balanced profile—high refractoriness, strong load-bearing capability, and reliable resistance against many common corrosive media.
Certification plays a quiet but decisive role here: it increases the probability that the brick you qualified is the brick you receive. That repeatability is the difference between a controlled maintenance plan and emergency patching.
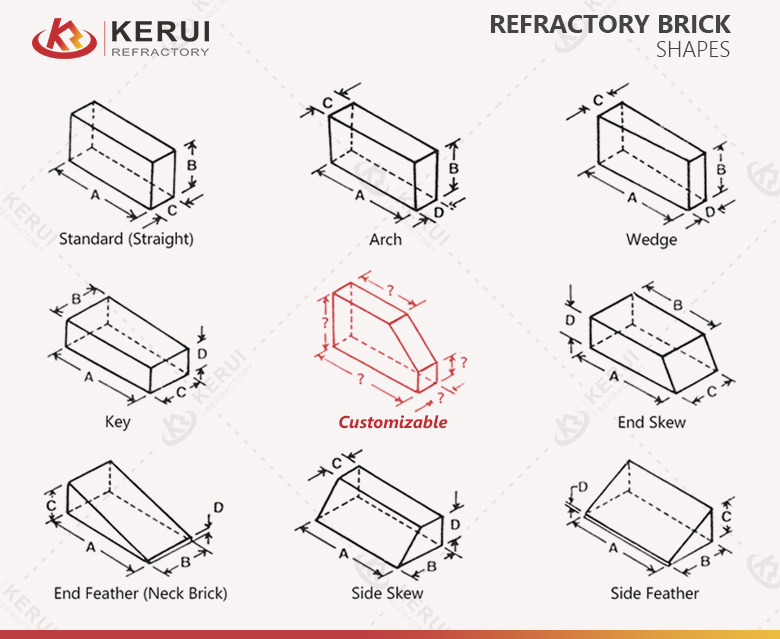
Large-scale plants (cement, metallurgy, glass, ceramics, chemical processing) typically run longer campaigns and face high downtime costs. The buying focus is not only on high-temperature rating, but also on batch-to-batch consistency, full documentation, and predictable wear behavior.
Smaller factories often deal with more frequent starts and stops, and may not have dedicated refractory engineers. Here, reliability and ease of selection matter most. A certified supplier reduces the learning curve and prevents costly mismatches.
In a kiln application facing intermittent operation and visible slag attack on the hot-face lining, an overseas buyer replaced a mixed-grade lining with a more consistent, certified supply of high alumina refractory bricks (75%+ Al2O3). After relining and following a controlled dry-out schedule, the plant reported:
While results depend on kiln design and operation, the pattern is consistent: certified manufacturing systems + correct alumina grade selection tends to reduce performance variability—the hidden driver of refractory cost.

Not always. 75%+ alumina is a strong baseline for many hot-face zones, but the best choice depends on slag chemistry, abrasion level, and thermal cycling. Some zones may require different formulations or grades to optimize cost and lifespan. A zone-based selection usually outperforms a single-grade approach.
Common requests include batch test reports (chemical analysis, CCS, porosity, bulk density), dimensional tolerance details, conformity documentation (for CE-related projects), and a packing list with batch/lot identification for traceability.
Spalling risk is often reduced by combining the right brick grade with correct installation practices: suitable refractory mortar, proper expansion joints, and a controlled dry-out/heating curve. Sharing your kiln’s operating temperature ramp rates and shutdown frequency helps the supplier recommend the most resilient grade.
Shortlist suppliers that can provide ISO 9001 documentation, clear product datasheets, consistent multi-lot testing evidence, and application references in similar kiln conditions. If your project touches EU compliance workflows, confirm CE-related documentation requirements early to avoid delays.
For buyers who want fewer surprises and more predictable kiln performance, RS Refractory supports selection with certification-backed production control and practical kiln-zone recommendations. Share your kiln type, working temperature, slag/ash conditions, and lining layout to receive a targeted recommendation.
Get a Technical Recommendation for RS High Alumina Refractory Bricks (75%+ Al2O3)Typical response includes suggested grade options, key performance targets, and documentation checklist for procurement.











